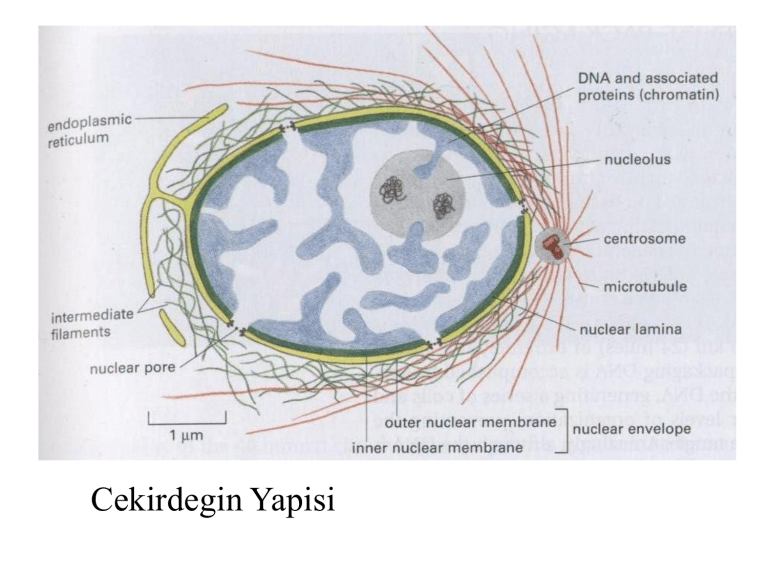
Cekirdegin Yapisi
Fig. x-x Electron micrograph of nucleus. Note absence of condensed (hetero)chromatin
under the pore. Also note the double membrane.
o Nukleer kilifin ic
membraninda katman
boyunca agsi bir yapi olusur.
o Nukleer lamina, 30-100 nm.
kalinliginda stabilize edici
ara filamentlerle cevrili.
o Bu ara filamentler agirligi
60-75 kD arasinda degisen
lamin polimerleridir.
o Laminler cekirdegin
fonksiyonel
organizasyonunda
gorevlidirler. Bunlar
mitozdan once ve sonra
katlanma ve acilmada
gorevlidirler.
•Laminler fosforile oldugu zaman, ayrisirlar.
Nukleer kilif vezikullerine ayrilir.
•Defosforilasyon ise bu durumu tersine cevirir ve
cekirdegin tekrar duzenlenmesi saglanir.
Nukleer Por Komplekslerinin SEM ile goruntulenmesi
Nukleer Por Kompleksi
Nuclear pore coplex (by negative staining and resulting model).
• Nukleer por kompleksi mRNA’yi tanir ve secici olarak olgun mRNA’nin
gecisine izin verir.
• Nukleer kisitlayici proteinler (RNA poly II, snRNP’ler, hnRNP/ intron
kompleksleri) nukleer cikistan hemen once uzaklastirilirlar.
• Mekik dokuyan proteinler(shuttling) mRNA’nin cikisina yardimci olmak icin
bagli kalirlar.(hnRNP A1, SR proteinleri, CBC)
• mRNA molekulunun cekirdekten cikisi Ran-Bagimli degildir. Fakat tRNA ve
snRNA’nin cikisi Ran-bagimlidir.
Transport of mRNA out of the nucleus. Different proteins can be found
associated with this abundant insect salivary gland mRNA inside and
outside of the nucleus.
Fig 4-23 EM of nucleosomes (B) and the 30nm chromatin fibre of packed
nucleosomes (A) in the normal conformation, which includes histone H1.
Nucleosome structure, except
histone H1 which causes
folding into the 30nm fibre.
Fig. x-x MODEL of DNA organization
around nucleosomes.
Each human cell nucleus contains
about 2m of DNA in 46 chromosomes
packed into about 10um diameter
nucleus.
Fig. 4-15 The size relationship between small human chromosome 22 (1.5% of
genome) and the gene number and size. There is a lot of repetitive and unused DNA.
STRUCTURE OF CHROMOSOMES AND DNA ORGANIZATION
Compare the highly condensed mitotic chromosome with relatively “loose” chromatin
of interphase nucleus. But even interphase chromatin is HIGHLY ORGANIZED:
supecoiled DNA and association with histone proteins in “nucleosomes”. In
Eukaryotes, this is in a number of linear chromosomes, with general structure shown
below:
Packaging DNA
Nucleosomes
11 nm
30 nm
Tight helical fiber
Metaphase
Chromosome
700 nm
200 nm Looped Domains
2 nm
B DNA Helix
Protein scaffold
